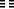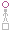Yi Jing 
 – I Ching, the Book of Changes
– I Ching, the Book of Changes
This famous system of 64 hexagrams plus their commentaries and transformations is at the root of Chinese thought. Tr. Wilhelm (en, fr).
| 29. K'an / The Abysmal (Water) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
current binomial swap trig. opposite flip X leading master X constituent master
The Hexagram
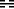
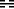
Above K'AN THE ABYSMAL, WATER
Below K'AN THE ABYSMAL, WATER
This hexagram consists of a doubling of the trigram K'an. It is one of the eight hexagrams in which doubling occurs. The trigram K'an means a plunging in. A yang line has plunged in between two yin lines and is closed in by them like water in a ravine. The trigram K'an is also the middle son. The Receptive has obtained the middle line of the Creative, and thus K'an develops. As an image it represents water, the water that comes from above and is in motion on earth in streams and rivers, giving rise to all life on earth.
In man's world K'an represents the heart, the soul locked up within the body, the principle of light inclosed in the dark–that is, reason. The name of the hexagram, because the trigram is doubled, has the additional meaning, "repetition of danger. " Thus the hexagram is intended to designate an objective situation to which one must become accustomed, not a subjective attitude. For danger due to a subjective attitude means either foolhardiness or guile. Hence too a ravine is used to symbolize danger; it is a situation in which a man is in the same pass as the water in a ravine, and, like the water, he can escape if he behaves correctly.
The Judgment
If you are sincere, you have success in your heart,
And whatever you do succeeds.
Through repetition of danger we grow accustomed to it. Water sets the example for the right conduct under such circumstances. It flows on and on, and merely fills up all the places through which it flows; it does not shrink from any dangerous spot nor from any plunge, and nothing can make it lose its own essential nature. It remains true to itself under all conditions. Thus likewise, if one is sincere when confronted with difficulties, the heart can penetrate the meaning of the situation. And once we have gained inner mastery of a problem, it will come about naturally that the action we take will succeed. In danger all that counts is really carrying out all that has to be done–thoroughness–and going forward, in order not to perish through tarrying in the danger.
Properly used, danger can have an important meaning as a protective measure. Thus heaven has its perilous height protecting it against every attempt at invasion, and earth has its mountains and bodies of water, separating countries by their dangers. Thus also rulers make use of danger to protect themselves against attacks from without and against turmoil within.
The Image
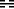
The image of the Abysmal repeated.
Thus the superior man walks in lasting virtue
And carries on the business of teaching.
Water reaches its goal by flowing continually. It fills up every depression before it flows on. The superior man follows its example; he is concerned that goodness should be an established attribute of character rather than an accidental and isolated occurrence. So likewise in teaching others everything depends on consistency, for it is only through repetition that the pupil makes the material his own.
Lower line
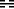
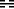
Repetition of the Abysmal.
In the abyss one falls into a pit.
Misfortune.
By growing used to what is dangerous, a man can easily allow it to become part of him. He is familiar with it and grows used to evil. With this he has lost the right way, and misfortune is the natural result.
Second line
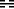
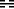
The abyss is dangerous.
One should strive to attain small things only.
When we are in danger we ought not to attempt to get out of it immediately, regardless of circumstances; at first we must content ourselves with not being overcome by it. We must calmly weigh the conditions of the time and be satisfied with small gains, because for the time being a great success cannot be attained. A spring flows only sparingly at first, and tarries for some time before it makes its way into the open.
Third line
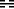
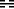
Forward and backward, abyss on abyss.
In danger like this, pause at first and wait,
Otherwise you will fall into a pit in the abyss.
Do not act this way.
Here every step, forward or backward, leads into danger. Escape is out of the question. Therefore we must not be misled into action, as a result of which we should only bog down deeper in the danger; disagreeable as it may be to remain in such a situation, we must wait until a way out shows itself.
Fourth line
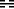
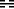
A jug of wine, a bowl of rice with it;
Earthen vessels
Simply handed in through the Window.
There is certainly no blame in this.
In times of danger ceremonious forms are dropped. What matters most is sincerity. Although as a rule it is customary for an official to present certain introductory gifts and recommendations before he is appointed, here everything is simplified to the utmost. The gifts are insignificant, there is no one to sponsor him, he introduces himself; yet all this need not be humiliating if only there is the honest intention of mutual help in danger.
Still another idea is suggested. The window is the place through which light enters the room. If in difficult times we want to enlighten someone, we must begin with that which is in itself lucid and proceed quite simply from that point on.
Fifth line
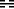
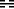
The abyss is not filled to overflowing,
It is filled only to the rim.
No blame.
Danger comes because one is too ambitious. In order to flow out of a ravine, water does not rise higher than the lowest point of the rim. So likewise a man when in danger has only to proceed along the line of least resistance; thus he reaches the goal. Great labors cannot be accomplished in such times; it is enough to get out of the danger.
Upper line
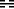
Bound with cords and ropes,
Shut in between thorn-hedged prison walls:
For three years one does not find the way.
Misfortune.
A man who in the extremity of danger has lost the right way and is irremediably entangled in his sins has no prospect of escape. He is like a criminal who sits shackled behind thorn hedged prison walls.
I Ching, the Book of Changes – Yi Jing I. 29. – Chinese off/on – Français/English
Alias Yijing, I Ching, Yi King, I Ging, Zhou yi, The Classic of Changes (Lynn), The Elemental Changes (Nylan), Le Livre des Changements (Javary), Das Buch der Wandlung.
The Book of Odes, The Analects, Great Learning, Doctrine of the Mean, Three-characters book, The Book of Changes, The Way and its Power, 300 Tang Poems, The Art of War, Thirty-Six Strategies
Welcome, help, notes, introduction, table.
Index – Contact – Top