Yi Jing 
 – I Ching, the Book of Changes
– I Ching, the Book of Changes
This famous system of 64 hexagrams plus their commentaries and transformations is at the root of Chinese thought. Tr. Wilhelm (en, fr).
| 35. Chin / Progress | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
current binomial swap trig. opposite flip X leading master X constituent master
The Hexagram
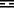
Above LI THE CLINGING, FIRE
Below K'UN THE RECEPTIVE, EARTH
The hexagram represents the sun rising over the earth. It is therefore the symbol of rapid, easy progress, which at the same time means ever widening expansion and clarity.
The Judgment

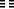
Is honored with horses in large numbers.
In a single day he is granted audience three times.
As an example of progress, this pictures a time when a powerful feudal lord rallies the other lords around the sovereign and pledges fealty and peace. The sovereign rewards him richly and invites him to a closer intimacy.
A twofold idea is set forth here. The actual effect of the progress emanates from a man who is in a dependent position and whom the others regard as their equal and are therefore willing to follow. This leader has enough clarity of vision not to abuse his great influence but to use it rather for the benefit of his ruler. His ruler in turn is free of all jealousy, showers presents on the great man, and invites him continually to his court. An enlightened ruler and an obedient servant–this is the condition on which great progress depends.
The Image

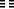
The image of PROGRESS.
Thus the superior man himself
Brightens his bright virtue.
The light of the sun rises over the earth is by nature clear. The higher the sun rises, the more it emerges from the dark mists, spreading the pristine purity of its rays over an ever widening area. The real nature of man is likewise originally good, but it becomes clouded by contact with earthly things and therefore needs purification before it can shine forth in its native clarity.
Lower line

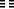
Progressing, but turned back.
Perseverance brings good fortune.
If one meets with no confidence, one should remain calm.
No mistake.
At a time when all elements are pressing for progress, we are still uncertain whether in the course of advance we may not meet with a rebuff. Then the thing to do is simply continue in what is right; in the end this will bring good fortune. It may be that we meet with no confidence. In this case we ought not to try to win confidence regardless of the situation, but should remain calm and cheerful and refuse to be roused to anger. Thus we remain free of mistakes.
Second line

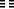
Progressing, but in sorrow.
Perseverance brings good fortune.
Then one obtains great happiness from one's ancestress.
Progress is halted; an individual is kept from getting in touch with the man in authority with whom he has a connection. When this happens, he must remain persevering, although he is grieved; then with a maternal gentleness the man in question will bestow great happiness upon him. This happiness comes to him–and is well deserved–because in this case mutual attraction does not rest on selfish or partisan motives but on firm and correct principles.
Third line

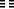
All are in accord. Remorse disappears.
A man strives onward, in association with others whose backing encourages him. This dispels any cause for regret over the fact that he does not have enough independence to triumph unaided over every hostile turn of fate.
Fourth line

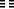
Progress like a hamster.
Perseverance brings danger.
In times of progress it is easy for strong men in the wrong places to amass great possessions. But such conduct shuns the light. And since times of progress are also times in which dubious procedures are inevitably brought to the light, perseverance in such action always leads to danger.
Fifth line

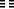
Remorse disappears.
Take not gain and loss to heart.
Undertakings bring good fortune.
Everything serves to further.
The situation described here is that of one who, finding himself in an influential position in a time of progress, remains gentle and reserved. He might reproach himself for lack of energy in making the most of the propitiousness of the time and obtaining all possible advantage. However, this regret passes away. He must not take either loss or gain to heart; they are minor considerations. What matters much more is the fact that in this way he has assured himself of opportunities for successful and beneficent influence.
Upper line

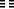
Making progress with the horns is permissible
Only for the purpose of punishing one's own city.
To be conscious of danger brings good fortune.
No blame.
Perseverance brings humiliation.
Making progress with lowered horns–i. e. , acting on the offensive–is permissible, in times like those referred to here, only in dealing with the mistakes of one's own people. Even then we must bear in mind that proceeding on the offensive may always be dangerous. In this way we avoid the mistakes that otherwise threaten, and succeed in what we set out to do. On the other hand, perseverance in such overenergetic behavior, especially toward persons with whom there is no close connection, will lead to humiliation.
I Ching, the Book of Changes – Yi Jing I. 35. – Chinese off/on – Français/English
Alias Yijing, I Ching, Yi King, I Ging, Zhou yi, The Classic of Changes (Lynn), The Elemental Changes (Nylan), Le Livre des Changements (Javary), Das Buch der Wandlung.
The Book of Odes, The Analects, Great Learning, Doctrine of the Mean, Three-characters book, The Book of Changes, The Way and its Power, 300 Tang Poems, The Art of War, Thirty-Six Strategies
Welcome, help, notes, introduction, table.
Index – Contact – Top